
Resin Documentationhome company docs
app server 
app server

amber
Amber is Resin's implementation of the JPA 1.0 persistence specification, focusing on simplicity and quality.
Example: House SQL create table HOUSE ( id integer auto_increment, name varchar(255) ) Example: House entity
package demo;
import javax.persistence.*;
@Entity
public class House {
@Id
@Column(name="id")
@GeneratedValue
private int _id;
@Basic
@Column(name="name")
private String _name;
}
Example: HouseServlet
package demo;
import javax.ejb.*;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.persistence.*;
public class HouseServlet extends GenericServlet {
@PersistenceUnit("test") EntityManagerFactory _factory;
public void load(PrintWriter out)
{
EntityManager amber = _factory.createEntityManager();
try {
House house = amber.find(House.class, 1);
out.println("House: " + house);
} finally {
amber.close();
}
}
public void query(PrintWriter out)
{
EntityManager amber = _factory.createEntityManager();
try {
Query query = amber.createQuery("select o from House o WHERE o.id=1");
out.println("House: " + query.getSingleResult());
} finally {
amber.close();
}
}
@TransactionAttribute
protected void insert(PrintWriter out)
{
EntityManager amber = _factory.createEntityManager();
try {
House house = new House("Gryffindor");
amber.persist(house);
} finally {
amber.close();
}
}
}
META-INF/persistence.xml <persistence xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence" version="1.0"> <persistence-unit name="test"> </persistence-unit> </persistence> WEB-INF/resin-web.xml
<web-app xmlns="http://caucho.com/ns/resin">
<ejb-server database="jdbc/test"/>
<servlet-mapping url-pattern="/test"
servlet-class="demo.HouseServlet"/>
</web-app>
EntityManagerjavax.persistence.EntityManager
public interface EntityManager {
public <T> T find(Class<T> entityCLass, Object primaryKey);
public <T> T getReference(Class<T> entityClass, Object primaryKey);
public void flush();
public <T> T merge(T entity);
public void persist(Object entity);
public void refresh(Object entity);
public void remove(Object entity);
public FlushModeType getFlushMode();
public void setFlushMode(FlushModeType flushMode);
public Query createQuery(String ql);
public Query createNamedQuery(String name);
public Query createNativeQuery(String sql);
public Query createNativeQuery(String sql, Class resultClass);
public Query createNativeQuery(String sql, String resultSEtMapping);
public void clear();
public void close();
public boolean contains(Object entity);
public Object getDelegate();
public boolean isOpen();
public EntityTransaction getTransaction();
public void joinTransaction();
public void lock(Object entity, LockModeType lockMode);
}
EntityManagerFactoryjavax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory
public interface EntityManagerFactory {
public EntityManager createEntityManager();
public EntityManager createEntityManager(Map map);
public void close();
public boolean isOpen();
}
EntityTransactionjavax.persistence.EntityTransaction
public interface EntityTransaction {
public void begin();
public void commit();
public void rollback();
public boolean getRollbackOnly();
public void setRollbackOnly();
public boolean isActive();
}
Queryjavax.persistence.Query
public interface Query {
public List getResultList();
public Object getSingleResult();
public int executeUpdate();
public Query setFirstResult(int startPosition);
public Query setFlushMode(FlushModeType flushMode);
public Query setHint(String hintName, Object value);
public Query setMaxResults(int maxResult);
public Query setParameter(String name, Object value);
public Query setParameter(String name, Date date, TemporalType type);
public Query setParameter(String name, Calendar date, TemporalType type);
public Query setParameter(int pos, Object value);
public Query setParameter(int pos, Date date, TemporalType type);
public Query setParameter(int pos, Calendar date, TemporalType type);
}
Class Annotations@DiscriminatorColumnConfigures the discriminator column, which select the entity class in an inheritance relationship. Each entity class will have a column value which uniquely selects the class to be loaded.
javax.persistence.DiscriminatorColumn
@Target(TYPE)
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface DiscriminatorColumn {
String name() default "";
DiscriminatorType discriminatorType() default STRING;
String columnDefinition() default "";
int length() default 31;
}
@EmbeddableAnnotates the class as an embeddable value. The class fields will represent a collection of table columns embedded as part of a containing class for the table. javax.persistence.Embeddable
@Target(TYPE)
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface Embeddable {
}
@EntityAnnotates the class as an entity bean. See the basic property tutorial and the basic field tutorial for an introduction.
javax.persistence.Entity
@Target(TYPE)
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface Entity {
String name() default "";
}
The fields or properties will be annotated by @Id, @Basic, etc. Amber will detect either field or property annotation by the type for the @Id. In other words, if Amber sees an @Id on a field, it will use field access. If Amber sees @Id on a method, it will use property access. @IdClassThe javax.persistence.IdClass
@Target({TYPE})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface IdClass {
Class value();
}
@Inheritance@Inheritance marks the entity bean as supporting inheritance, i.e. the database maps to different Java classes depending on a discriminator value.
javax.persistence.Inheritance
@Target(TYPE)
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface Inheritance {
InteritanceType strategy() default SINGLE_TABLE;
}
@MappedSuperclassThe javax.persistence.MappedSuperclass
@Target({TYPE})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface MappedSuperclass {
}
@SecondaryTableSpecifies a secondary database table for an entity bean. The secondary table will contain the fields with a secondaryTable in the @Column.
javax.persistence.SecondaryTable
@Target(TYPE)
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface SecondaryTable {
String name() default "";
String catalog() default "";
String schema() default "";
PrimaryKeyJoinColumn []pkJoinColumns() default {};
UniqueConstraint []uniqueConstraints() default {};
}
@SequenceGeneratorSpecifies a sequence table to be used for generating keys.
javax.persistence.SequenceGenerator
@Target({TYPE, METHOD, FIELD})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface SequenceGenerator {
String name();
String sequenceName() default "";
int initialValue() default 0;
int allocationSize() default 50;
}
@TableSpecifies the database table for an entity bean. The default table name is the class name.
package javax.persistence;
@Target(TYPE)
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface Table {
String name() default "";
String catalog() default "";
String schema() default "";
UniqueConstraint []uniqueConstraints() default {};
}
@TableGeneratorSpecifies a secondary table to be used for generating keys.
javax.persistence.TableGenerator
@Target({TYPE, METHOD, FIELD})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface TableGenerator {
String name();
String table() default "";
String catalog() default "";
String schema() default "";
String pkColumnName() default "";
String valueColumnName() default "";
String pkColumnValue() default "";
int initialValue() default 0;
int allocationSize() default 50;
UniqueConstraint []uniqueConstraints() default {};
}
Property Annotations@BasicMarks a field as a persistent field.
javax.persistence.Basic
@Target({METHOD, FIELD})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface Basic {
FetchType fetch() default EAGER;
boolean optional() default true;
}
The fetch types are:
Example: string property
@Entity
public class Course {
@Basic
public String getName()
...
}
Example: lazy-loaded property
@Entity
public class Course {
@Basic(fetch=FetchType.LAZY)
public String getMassiveText()
...
}
@ColumnSpecifies the field's SQL column name as well as any CREATE TABLE properties for auto generation.
javax.persistence.Column
@Target({METHOD, FIELD})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface Column {
String name() default "";
boolean unique() default false;
boolean nullable() default true;
boolean insertable() default true;
boolean updateable() default true;
String columnDefinition() default "";
String table() default "";
int length() default 255;
int precision() default 0;
int scale() default 0;
}
Example: @Column for a string property
@Entity
public class Course {
@Basic
@Column(name="MY_NAME",
unique=true,
nullable=false,
length=32)
public String getName()
...
}
@EmbeddedMarks a field as containing an embeddable value. The field's value will be a class marked as @Embeddable. Applications can use @Embedded fields to gather columns into meaningful groups. javax.persistence.Embedded
@Target({METHOD, FIELD})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface Embedded {
}
@EmbeddedIdMarks a field as a primary key with a embedded class. The field's
value class must be marked with javax.persistence.EmbeddedId
@Target({METHOD, FIELD})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface EmbeddedId {
}
@EnumeratedMarks a field as containing an enumerated value.
javax.persistence.Enumerated
@Target({METHOD, FIELD})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface Enumerated {
EnumType value() default ORDINAL;
}
@GeneratedValueUsed with @Id to specify a generator for automatic key generation when new objects are created.
The generator types are:
javax.persistence.GeneratedValue
@Target({METHOD, FIELD})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface GeneratedValue {
GenerationType strategy() default AUTO;
String generator() default "";
}
For SEQUENCE and TABLE, Resin will create the sequence name as "${'${'}table}_cseq". Example: autoincrement generation
import javax.persistence.*;
@Entity
public class Course {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
public long getId()
...
}
Example: sequence generation
import javax.persistence.*;
@Entity
public class Course {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GeneratorType.AUTO
generator="COURSE_SEQ")
public long getId()
...
}
@IdMarks a field as a primary key. The javax.persistence.Id
@Target({METHOD, FIELD})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface Id {
}
The default column name is "ID". Example: automatic generation
import javax.persistence.*;
@Entity
public class Course {
@Id
@Column(name="t_id")
@GeneratedValue
public long getId()
...
}
@LobMarks a field as containing a large blob value. javax.persistence.Lob
@Target({METHOD, FIELD})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface Lob {
}
@TemporalMarks a field as a time-based value.
javax.persistence.Temporal
@Target({METHOD, FIELD})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface Temporal {
TemporalType value() default TIMESTAMP;
}
Relation annotations@JoinColumnDefines a join (foreign) columns. Used for @ManyToOne. See also @Column for corresponding definition for @Basic columns. See the Many-to-One tutorial for a full example.
javax.persistence.JoinColumn
@Target({TYPE, METHOD, FIELD})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface JoinColumn {
String name() default "";
String referencedColumnName() default "";
boolean unique() default false;
boolean nullable() default false;
boolean insertable() default true;
boolean updateable() default true;
String columnDefinition() default "";
String table() default "";
}
Example: Student to House link
public class Student {
@Id
@Column(name="student_id")
long getId()
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name="house_id")
public House getHouse()
}
Example: Student SQL
CREATE TABLE Student {
student_id BIGINT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment
house_id BIGINT REFERENCES House(id)
)
@JoinColumnsDefines a set of join (foreign) columns for composite keys. javax.persistence.JoinColumns
@Target({TYPE,METHOD, FIELD})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface JoinColumns {
JoinColumn [] value() default{}
}
@JoinTableDefines an association table for a many-to-many relation.
javax.persistence.JoinTable
@Target({METHOD, FIELD})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface JoinTable {
String table() default "";
String catalog() default "";
String schema() default "";
JoinColumn []joinColumns() default {};
JoinColumn []inverseJoinColumns() default {};
UniqueContraint []uniqueConstraint() default {};
}
@ManyToManyMarks a field as a many-to-many (association) relation. The column names are the key columns of the source and target tables. See the many-to-many tutorial for an example.
javax.persistence.ManyToMany
@Target({METHOD, FIELD})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface ManyToMany {
String targetEntity default "";
CascadeType []cascade() default {};
FetchType fetch() default LAZY;
String mappedBy isInverse() default "";
}
Example: @ManyToMany link
@Entity
public class Student {
@ManyToMany
@JoinTable(
name="student_course_map",
joinColumns={@JoinColumn(name="student_id")},
inverseJoinColumns={@JoinColumn(name="course_id")}
)
public Collection getCourses()
...
}
@ManyToOneMarks a field as a many-to-one (link) relation. The default column name is the column name of the target key. See the many-to-one tutorial for an example.
javax.persistence.ManyToOne
@Target({METHOD, FIELD})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface ManyToOne {
String targetEntity default "";
CascadeType []cascade() default {};
FetchType fetch() default EAGER;
boolean optional() default true;
}
Example: @ManyToOne link
@Entity
public class Student {
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name="house")
public House getHouse()
...
}
@MapKeyMarks a field as key in a Map relationship. javax.persistence.MapKey
@Target({METHOD, FIELD})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface MapKey {
String name() default "";
}
@OneToManyMarks a field as a one-to-many (collection) relation. Because a one-to-many field is dependent, it needs a @ManyToOne relation on the source table which defines the column.
javax.persistence.OneToMany
@Target({METHOD, FIELD})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface OneToMany {
String targetEntity default "";
CascadeType []cascade() default {};
FetchType fetch() default EAGER;
String mappedBy() default "";
}
Example: collection
@Entity
public class House {
...
@OneToMany(targetEntity=Student.class,
mappedBy="house")
public Collection getStudents()
}
@Entity
public class Student {
...
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name="house")
public House getHouse()
}
Example: Collection SQL
CREATE TABLE House {
id BIGINT PRIMARY KEY
)
CREATE TABLE Student {
id BIGINT PRIMARY KEY,
house BIGINT REFERENCES House(id)
)
@OneToOneMarks a field as a one-to-one (dependent link) relation. Because a one-to-one field is dependent, it needs a @ManyToOne relation on the source table which defines the column.
javax.persistence.OneToOne
@Target({METHOD, FIELD})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface OneToOne {
String targetEntity default "";
CascadeType []cascade() default {};
FetchType fetch() default EAGER;
boolean optional() default true;
String mappedBy() default "";
}
@OrderBy
javax.persistence.OrderBy
@Target({METHOD, FIELD})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface OrderBy {
String value() default "";
}
Non-Transactional LifecycleAmber's non-transactional lifecycle has three important states:
In the diagram below, the red methods ( 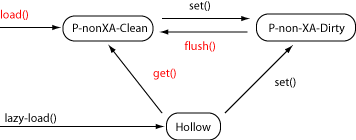 The Calling Calling The state represents lazily-loaded entities. many-to-one
relations and some queries will return the unloaded bean instead of
a loaded bean. When the application calls a Example: Amber outside transaction
public class MyServlet extends GenericServlet {
@In EntityManagerFactory _factory;
@In UserTransaction _trans;
...
public void doTest(PrintWriter out)
throws IOException
{
EntityManager aConn = _factory.createManager();
// load() loads test and then detaches it
qa.Test test = aConn.load(qa.Test.class, "1");
// test has the loaded values
out.println(test.getData());
// but parent is not lazily-loaded when detached, i.e. it's null.
qa.Test parent = test.getParent();
aConn.close();
}
}
Transactional LifecycleIn a transaction, Amber loads the bean from the database, even if it was loaded outside of the transaction. (Exceptions exist for cases like read-only beans.) By loading the bean in the transaction, Amber lets the database handle the transactional locking and state consistency. Just like the non-transactional and states, Amber has transactional and states called and . As in the non-transactional case, the state represents lazily-loaded beans.
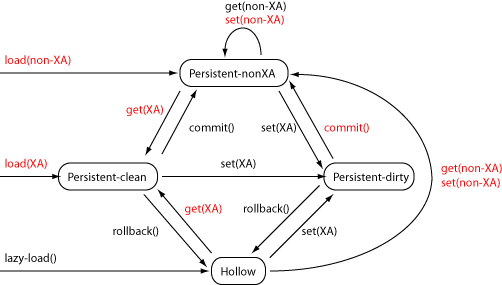 The main differences from the non-transactional lifecycle are:
Example configurationThe lifecycle description uses a single running example, Test, which
has two properties: Example: META-INF/orm.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<entity-mappings xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence/orm"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence/orm orm_1_0.xsd"
version="1.0">
<package>qa</package>
<entity name="Test" class="qa.Test" access="PROPERTY">
<table name="TEST"/>
<attributes>
<id name="id">
<column name="ID"/>
</id>
<basic name="data">
<column name="DATA"/>
</basic>
<many-to-one name="parent">
<join-column name="FK_PARENT"/>
</many-to-one>
</attributes>
</table>
</entity>
</entity-mappings>
|